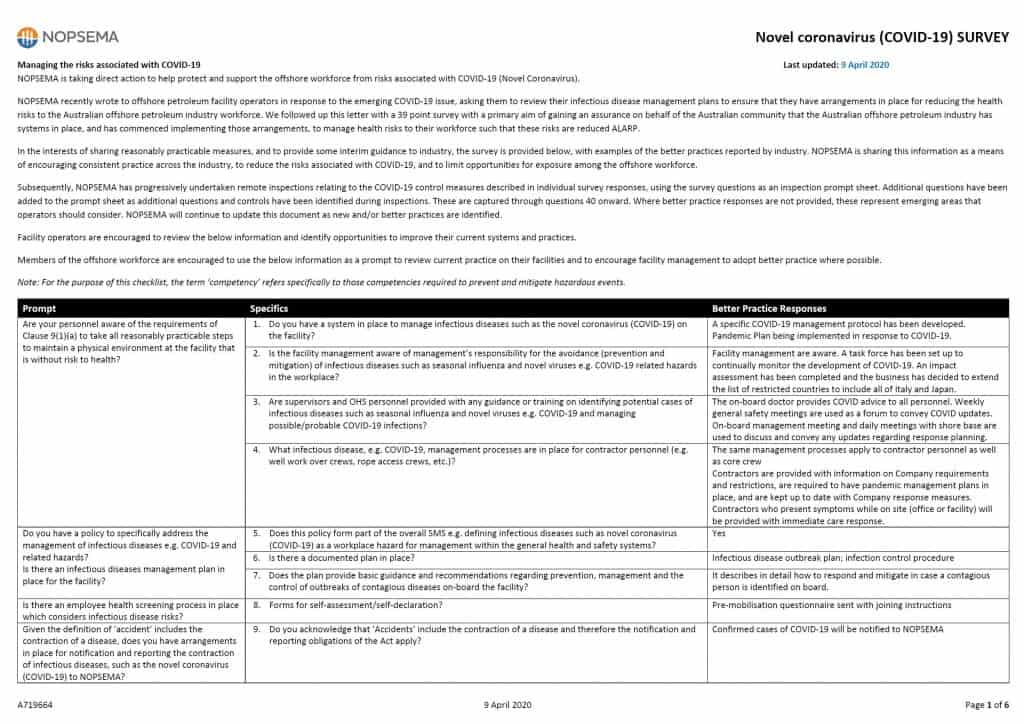
Brittany Higgins alleges that she was raped in her employer’s office by a work colleague after a night of drinking. Since mid-February 2021, other women have claimed to have been sexually assaulted in Parliament. The Attorney-General, Christian Porter, is taking some leave after revealing himself to be the person behind historical rape allegations. At the moment, Australian politics is wrapped up in itself over these scandals. Still, similar scandals have happened in other Parliaments, and the responses to these may provide guidance for Australia.
A small survey of female parliamentarians and staff in Europe in 2018 found the following
▪ 85.2 per cent of female MPs who took part in the study said that they had suffered psychological violence in the course of their term of office.
▪ 46.9 per cent had received death threats or threats of rape or beating.
▪ 58.2 per cent had been the target of online sexist attacks on social networks.
▪ 67.9 per cent had been the target of comments relating to their physical appearance or based on gender stereotypes.
▪ 24.7 per cent had suffered sexual violence.
▪ 14.8 per cent had suffered physical violence.