Yesterday morning, Mike Hammond of the Australian law firm, Norton Rose, conducted a seminar on the harmonisation of Australia’s work health and safety laws. This was the last in the current series of seminars on this topic but Hammond’s seminar differed considerably from previous sessions. Hammond is clearly less than enamoured with the model Work Safety and Health Act, describing parts of the legislation as “bad law” and asking whether the laws were examples of “social engineering”.
Understandably, these comments generated considerable discussion from the audience of around 50 people.
The crucial nub of Hammond’s concerns was the lack of essential definitions in the model law. Continue reading “Labor lawyer raises strong concerns over new Work Health and Safety laws”

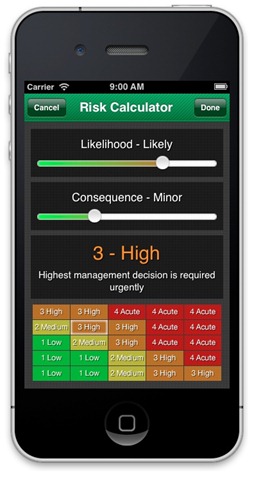

 Safe Work Australia has released a couple of packages of draft codes of practice in line with the Australian Government’s OHS harmonisation strategy but where is the code that addresses the established risk of environmental tobacco smoke (ETS) or second-hand smoke? This is a question that was asked during the recent Safe Work Australia week by
Safe Work Australia has released a couple of packages of draft codes of practice in line with the Australian Government’s OHS harmonisation strategy but where is the code that addresses the established risk of environmental tobacco smoke (ETS) or second-hand smoke? This is a question that was asked during the recent Safe Work Australia week by 