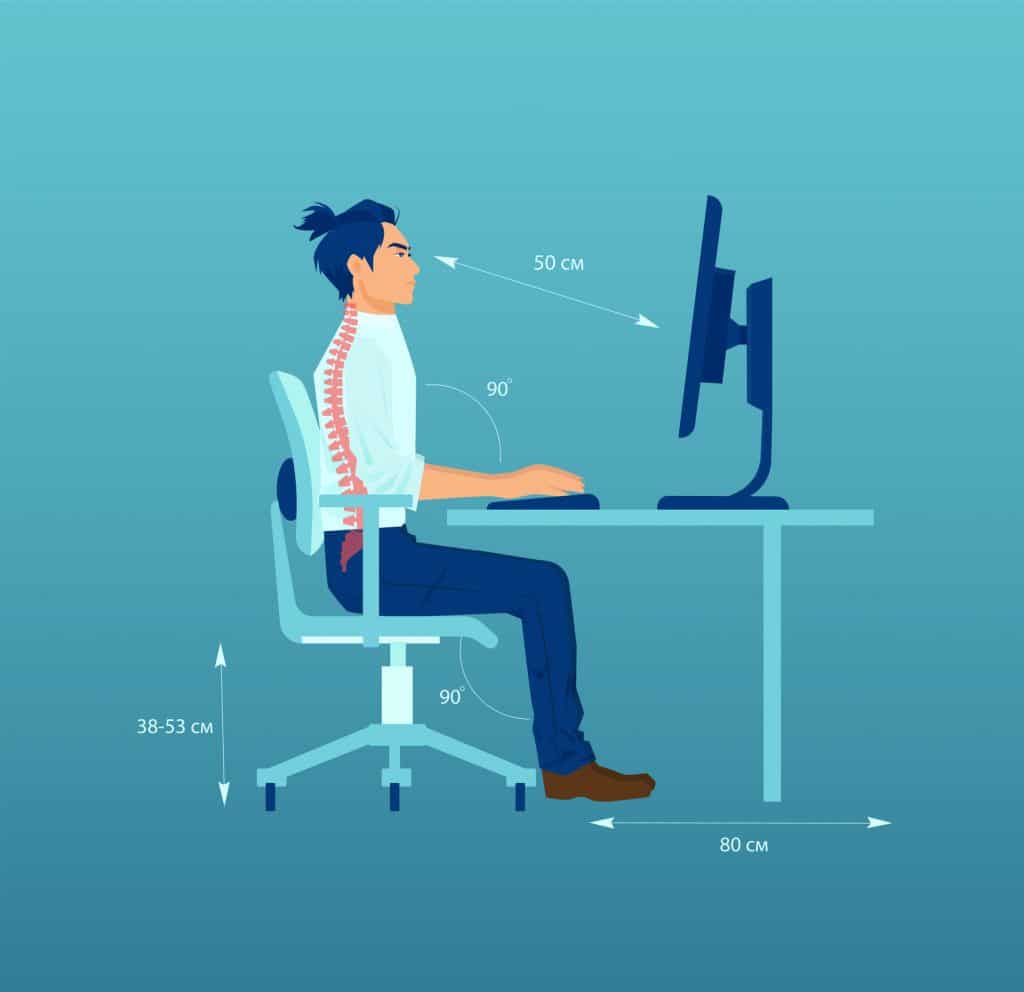
Earlier this year Dr Peter Sharman published a blog article based on a literature review related to Upper Limb Pain and Computer Employment. The ergonomics of desk-based work seems to be dominated by guidance that requires right-angled postures, and other practices that are designed for prolonged use. For most of us, there is the flexibility to move around and break up the tasks but workplace, like call centres, continue; and the recent move to work from home has resurrected many of these workstation advisories. SafetyAtWorkBlog had the opportunity to ask Dr Sharman about his research and his experience supplemented by some clarifying answers by retired consultant in rheumatology and pain medicine, John Quintner.