Official statistics on workplace bullying in Australia are notoriously unreliable. The Productivity Commission estimated the cost of workplace bullying with a huge margin of variation, between A$6 billion and A$36 billion annually. WorkSafe Victoria has indicated in the past that the number of interventions on workplace bullying is way below the number of workplace bullying complaints. On 29 October 2103, in a long discussion on workplace bullying the Australian Capital Territory’s Chief Minister, Katy Gallagher stated:
“According to reports from the Commissioner for Public Administration, reports of bullying and harassment have totalled 68 cases in 2010-11, 71 in 2011-12, and 118 cases in the financial year that has just passed, 2012-13. Proven cases of bullying have numbered four, eight 11 and 19 respectively. This amounts to complaints being made by 0.5 per cent of staff, and substantiated in relation to 0.08 per cent of staff.” (Hansard, page P3930, emphasis added)
These latest statistics, in conjunction with those previously reported, indicate that the perception of workplace bullying is much higher than the reality in Australia. Continue reading “Fair Work Commission girds its loins for workplace bullying complaints”

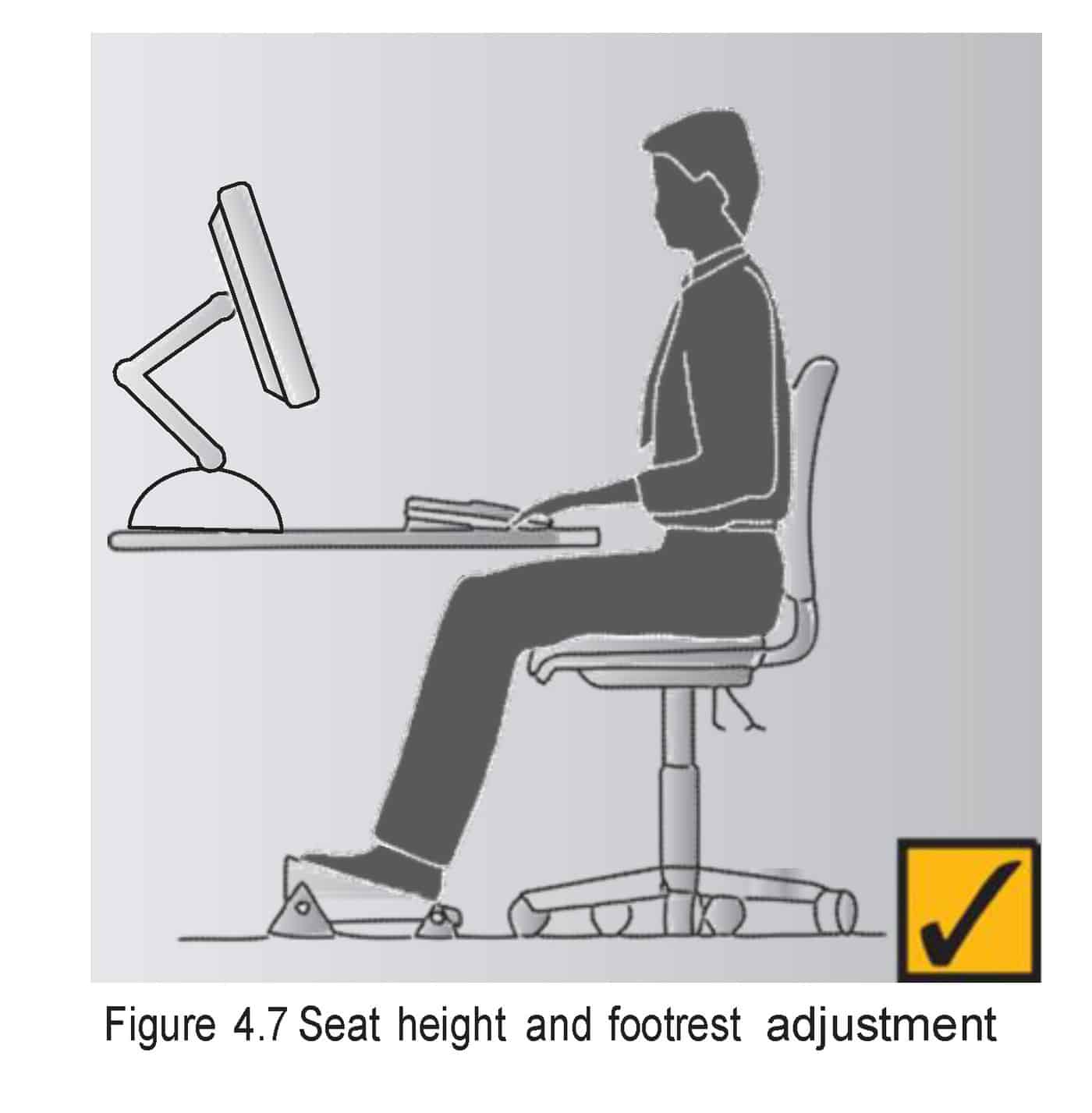 A diagram of safe posture at modern workstations has become iconic but it has also become a symbol of ergonomic misunderstanding. There are assumptions behind the angular figure about the way modern workers work, the equipment used and the tasks undertaken.
A diagram of safe posture at modern workstations has become iconic but it has also become a symbol of ergonomic misunderstanding. There are assumptions behind the angular figure about the way modern workers work, the equipment used and the tasks undertaken. As the 1 January 2014 implementation date for new
As the 1 January 2014 implementation date for new 