Business ethics has never been a significant focus of occupational health and safety (OHS) organisations or regulators beyond what the law says. OHS advisers in companies and through consultation constantly address ethical or unethical behaviour, even though this is rarely discussed at the academic level or outside of the possibility of prosecution. Over the last four decades, neoliberal ideology and policies have given OHS only grudging attention, if any at all. Neoliberalism is gaining more attention in the OHS literature as the socioeconomic and political sources of hazards are finally receiving serious attention. However, most OHS people cannot remember a world before neoliberalism. It is important to remember that trust in the “free market’ on which neoliberalism was built, the promises of wealth for all, and reflect on how worker health and safety suffered.
Category: neoliberalism
Mental health, neoliberalism and trade union myopia
The Australia Institute is a progressive (Left-leaning) research institute that recently commemorated its 30th anniversary with a book called “What’s the Big Idea?” Contributors are compatible with the Institute’s ideologies, but some chapters overlap with occupational health and safety (OHS).
Business values and OHS impacts
No one outside occupational health and safety (OHS) talks about OHS. Outside of scandals and disasters, OHS is a fringe consideration, especially in the media—social and mainstream. So, OHS needs to insert itself into mainstream conversations. The column by economics journalist Ross Gittins in The Age newspaper on September 23, 2024, says much about OHS without mentioning it.
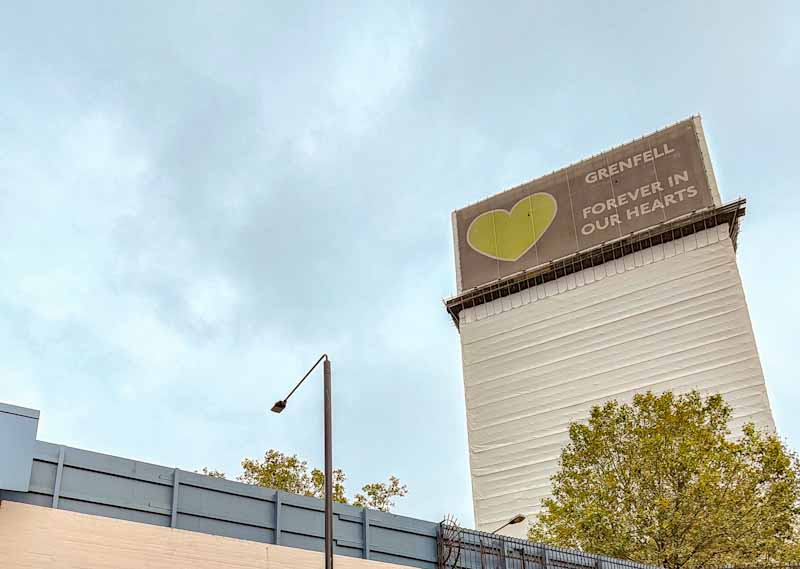
“…the system isn’t broken. It was built this way” – Grenfell Tower and OHS
The inquiry report into the Grenfell Tower fire has yet to be seriously considered from the other side of the world. However, the report is being mentioned in Australia’s emergency services and fire sectors. The inquiry has been thoroughly followed and analysed in the United Kingdom, and many excellent summaries have been published in newspapers, books, and podcasts. Australia’s cladding debate has not been to the same extent as the UK. Still, the UK’s structures, policies, processes, business ethics and neglect are certainly mirrored in Australia, which directly impacts how workplace health and safety operates here.
We must understand the social pressures on employer safety decisions
There is a cost-of-living crisis in large parts of the world, there is a climate emergency, there are wars and political instability and insecurity everywhere. Why is occupational health and safety (OHS) still considered important? Well, it isn’t really when compared to these global and existential crises, but that is the microcosm in which we operate. However, this does not mean we should withdraw into our safety shells and ignore the world. We can’t; the world intrudes on our microcosm and affects us directly and indirectly.
So, it is useful to understand how pressures external to our work and workplaces affect our choices and the choices of employers.
A broad perspective on Work, OHS and Mental Health
A whole generation of workers has grown up believing that if they are having a hard time at work, if they are not coping with the workload or the sexual advances of their boss, or their difficult workplace, or the discrimination they feel about their gender or their sexuality, that it’s their fault, and it’s their problem, and therefore, it’s their role to solve and fix it. But there were generations before the current one, and I’m from one of those earlier generations. When I started work, there was good work and safe jobs, and there were social movements for women’s rights, and then gay rights and dignity at work, and respect at work. It was far from a paradise, but there was exciting progress and lively, challenging debates and social protests. A little of that passion has returned this decade, but more is needed.
Broadening the OHS perspective
Over the last decade, the occupational health and safety (OHS) profession has been challenged by a new perspective on OHS and its professional interaction with it. Safety Differently, Safety II or some other variation are important and intriguing variations, but they seem to remain confined to the workplace, the obligations of the person conducting a business or undertaking, and/or the employer/employee relationship. The interaction of work and non-work receives less attention than it deserves.
Many OHS professionals bemoan OHS’ confinement to managerial silos but continue to operate within their own self-imposed silo. One way for OHS to progress and to remain current and relevant is to look more broadly at the societal pressures under which they work and how their employees or clients make OHS decisions. Some recent non-OHS books and concepts may help.