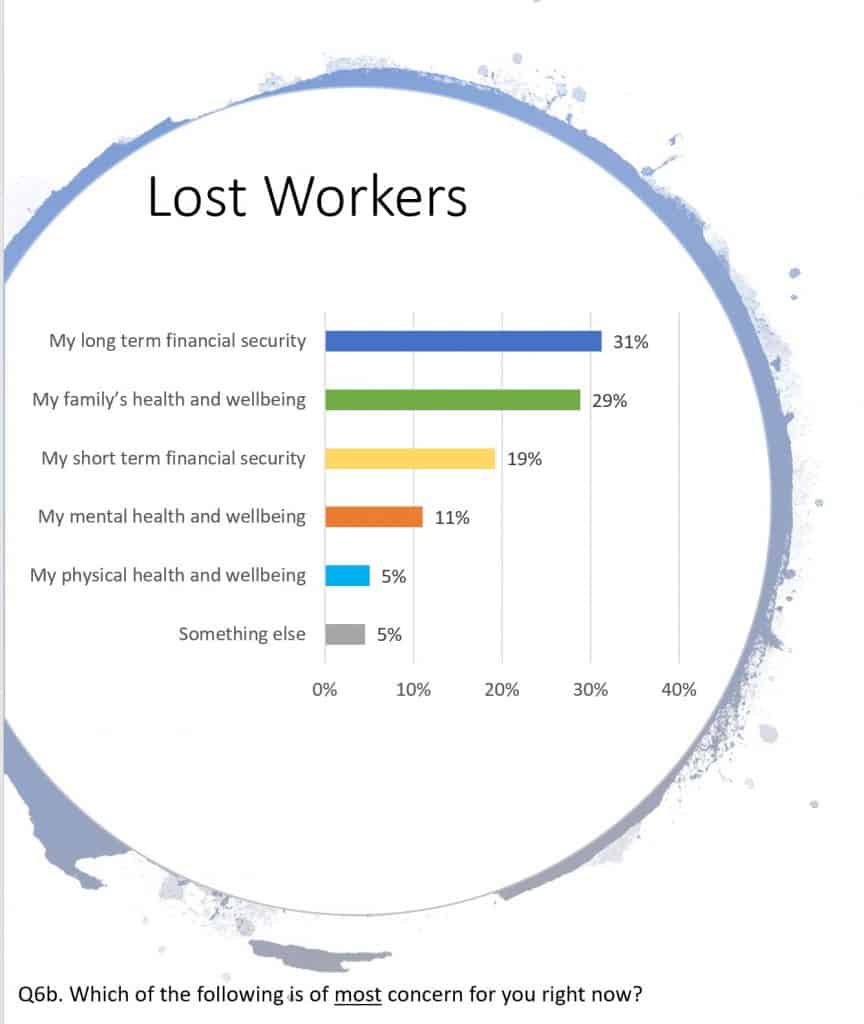
Last week the Australian Council of Trade Unions (ACTU) released some research into workers and COVID19. It is not peer-reviewed and there will certainly be much more research into the disruption and personal and occupational responses to the coronavirus disruption over the next few months. The survey results do not specifically analyse occupational health and safety (OHS) issues but there are clues to future considerations.
The media release, understandably, discusses the changed employment status or arrangements. The OHS hazards associated with precarious work are well-established and the survey illustrates the extent of precarity in Australian workplace, so mental health issues are going to come to the fore as government-imposed isolation continues and/or businesses reopen.






