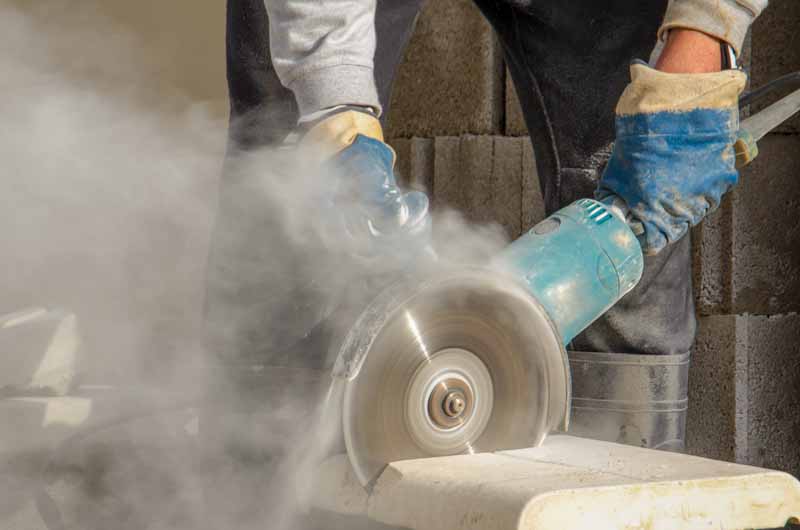
In 2019, Dr Graeme Edwards said this of the cutters of engineered stone:
“We can’t just rely on the industry to self-regulate. We need to licence the industry and we need to regulate the product….. If we can’t do this, [banning] is a realistic option.”
Recent research commissioned by the Australian Council of Trade Unions (ACTU) and conducted by Curtin University seems to support a ban on the import of engineered stone products with such a high level of silica that cutting them, without suitable controls, can lead to silicosis.