Niru Tyagi recently wrote on LinkedIn about Denmark’s regulatory approach to work-related psychosocial hazards, comparing it the current Australian approach, framing Denmark as creating an industrial obligation. It is a perceptive comparison but downplays the significance in Australia of the criterion of reasonably practicable.
Category: employers
Pop Psychology Isn’t a Safety Strategy
Last week, I attended a webinar on psychological safety that confirmed all of my worst fears about the Human Resources approach to addressing psychosocial factors and mental health at work.
When Safe Work Month Shrinks and Psychosocial Hazards Expand
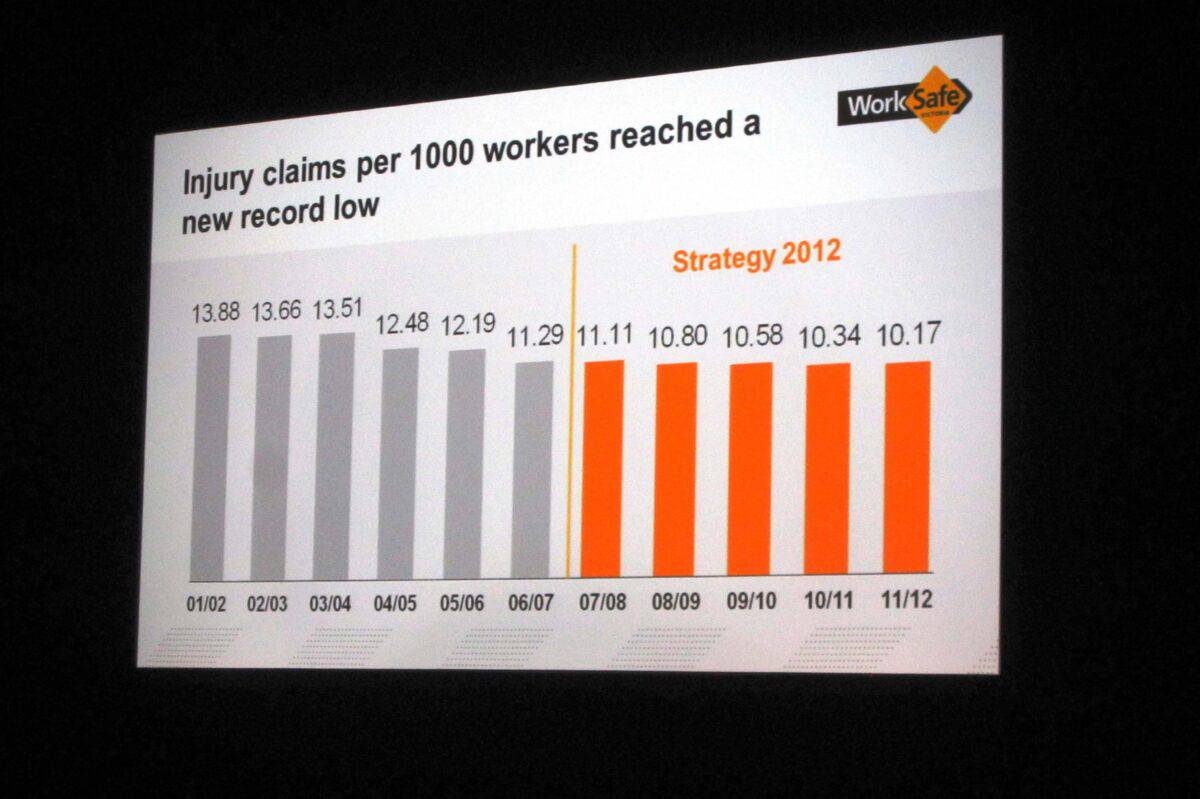
WorkSafe Victoria used to launch National Safe Work Month (or Safe Work Week as it started out) in a big way in Melbourne. They tried something similar when it relocated to Geelong, but this year, there was nothing of the same magnitude. There was some strong publicity benefit from having a big half- to full-day event at the start, but apparently, there was no additional benefit beyond that.
I would argue that the big event for this year’s safety month is the “Psychological Health Regulations: A focus on risk management” webinar on October 27, 2025. The new regulations and Compliance Code are what everyone seems to be talking about. For contrast, I have reviewed some of the presentations from the opening of WorkSafe Week in October 2012 by WorkSafe and VECCI.
OHS and Politics
In support of Australia’s Safe Work Month, I have recorded a 12-minute opinion piece on how Australian politics since 2010 has affected the perception and development of occupational health and safety, based on past SafetyAtWorkBlog articles.
It is an interesting opportunity to reflect on the decisions and actions of influential individuals like Julia Gillard, Kristina Keneally, Jeff Lawrence, and David Gregory.
Workplace safety reform is happening but you probably won’t hear about it in the headlines
Occupational health and safety (OHS) can feel like a humdrum career when working in a low-risk, well-managed organisation. But the wheels of change roll on. Here’s a quick sample of some of that activity over the last week or so that you are unlikely to see elsewhere.
When Leadership Fails the Soul
Dean Yates is a prominent Australian speaker on the issue of moral injury. Yesterday, at a WorkSafe Tasmania seminar, Yates brought the 250 attendees up to date on the status of moral injury and its occupational context. Although this seminar was a Safe Work Month event, Yates’ information requires some thought to fit with the occupational health and safety (OHS) and psychological hazards contexts.
Culture is the New Compliance in Victoria’s Psychological Health Code
The most significant challenges for employers in Victoria’s new OHS (Psychological Health) Regulations, supported by a new Compliance Code, are likely to be fostering a strong workplace safety culture. Occupational health and safety (OHS) advocates have been emphasising the importance of culture for several decades now (Sociologists examined it decades before). It appears that we will be hearing a great deal more about culture for some time to come, but what is expected of employers?