Business newspapers and websites often report on executives revealing their own burnout and how they have changed their lives as a result. The changes they make indicate their decisions that led to their mental health crises and epiphanies. But executives lead by example, so how many of the employees are emulating the executives’ mistakes? Shouldn’t the executives redesign their companies’ systems of work to prevent anyone else from suffering from burnout?
Category: law
Is Defence Above Safety Scrutiny? Lambie Wants to Know
Senator Jacquie Lambie has been a staunch advocate for improving the occupational health and safety (OHS) of Australia’s defence force personnel. In 2022, she gave a confronting presentation to the Royal Commission into Defence and Veteran Suicide, and she continued her advocacy on day 1 of the 48th session of the Australian parliament by asking reasonable questions that could also be posed in non-military industries.
Breaking the Silence: Dekker’s Call for Authentic Voice in OHS
Any new book from Sidney Dekker is worth reading. His latest is called “Safety Theater – How the Desire for Perfection Drives Compliance Clutter, Inauthenticity, and Accidents”. I am not sure that this book, the third in a series, offers solutions, but it reframes many of the contemporary perspectives on occupational health and health and safety (OHS), and with some intriguing connections.
Reform or Reframe? NSW’s WHS Laws Tackle Liability, Not Prevention
The New South Wales (Labor) government has amended its work health and safety and industrial relations laws. These changes have been described as “substantial” in one legal opinion, but the changes reflect the management of company liability more than preventing harm.
Fear, Trust, and the Cost of Control
CCTV cameras on a cash register may deter theft due to the fear of consequences, such as discipline or dismissal, but they also communicate a lack of trust. If the aim is to prevent physical actions like theft, they work. But can they prevent occupational health and safety (OHS) breaches like sexual abuse in childcare centres?
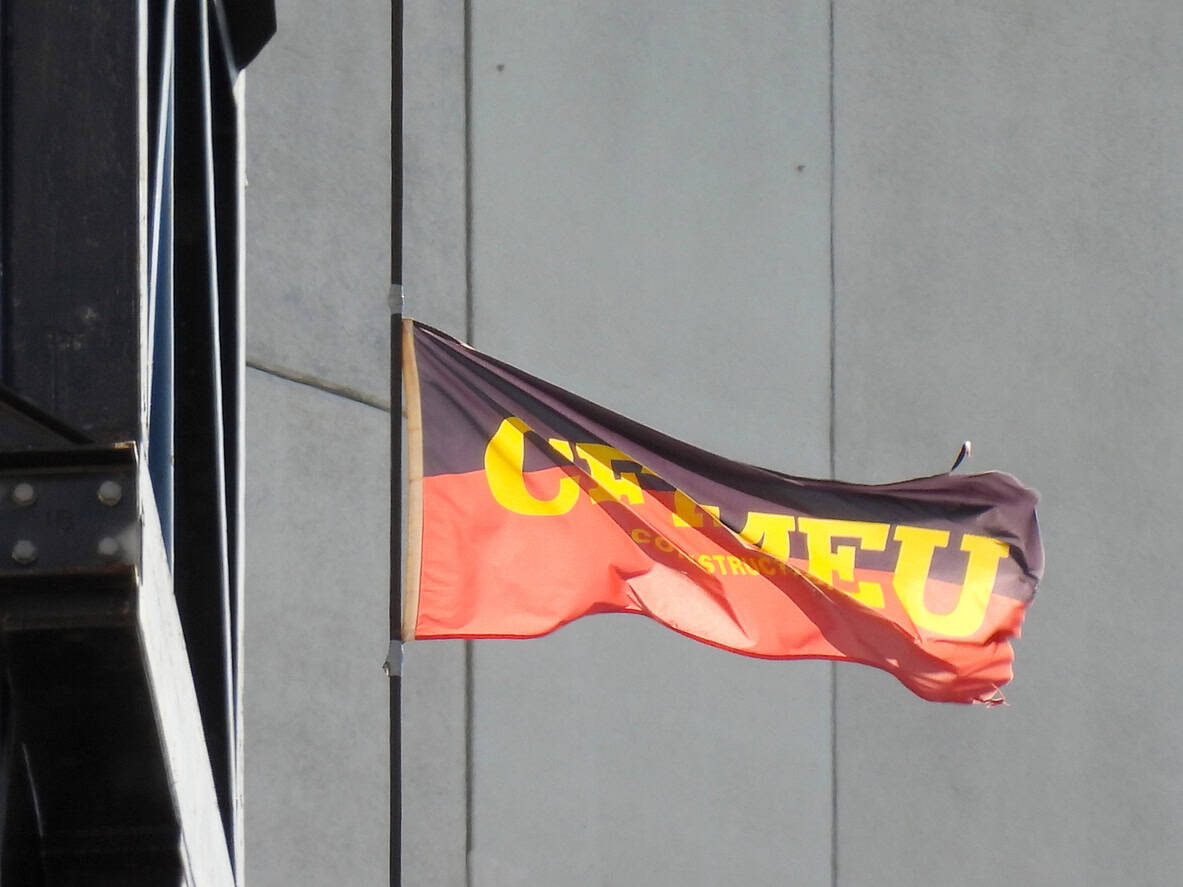
Confronting Union Thuggery that Undermines Workplace Safety
Militant construction unions in Australia have damaged the relationship between the community and the trade union movement. Although the typical trade union member may be a nurse, a teacher, or a public servant, most would depict a member as a big, aggressive, rude, and domineering man. Australia’s trade union movement is trying to redress this perception, but it cannot progress until it eliminates the unsafe behaviour of the organisers of the Construction Forestry Mining and Energy Union (CFMEU). The Queensland government is set to give reform a red-hot go.
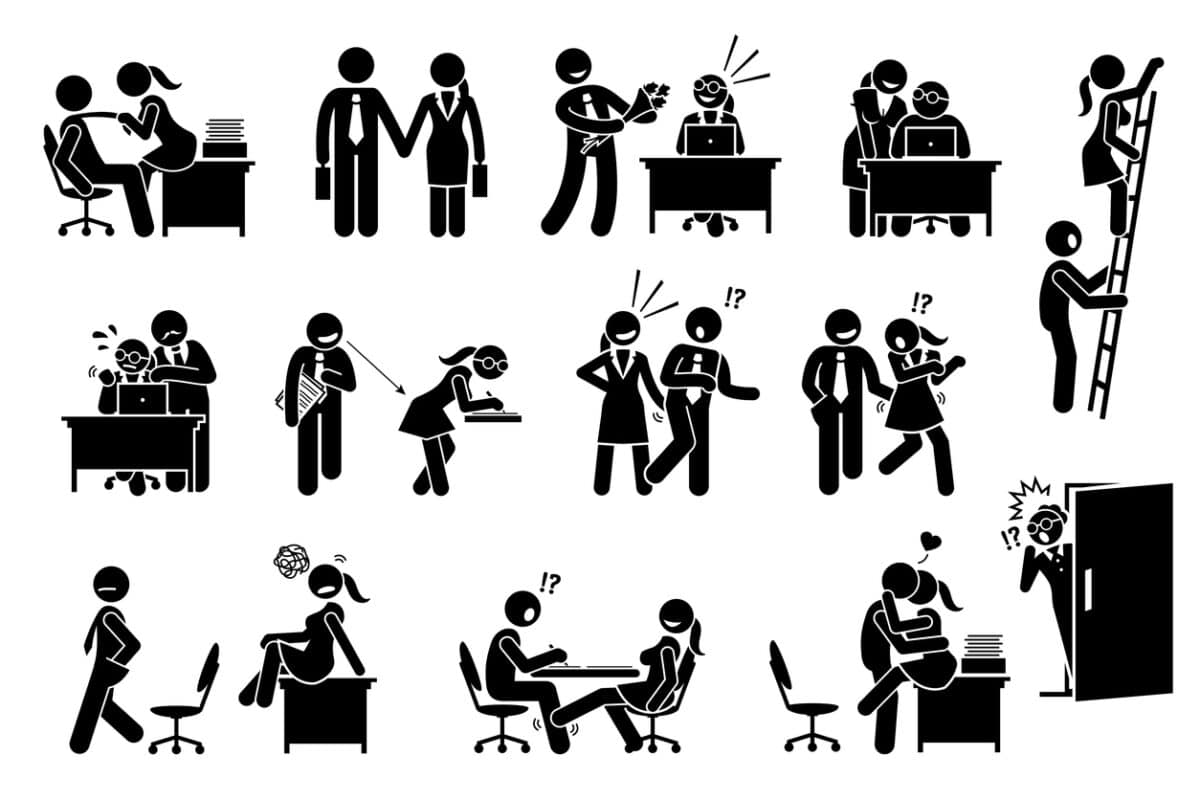
Sexual Harassment Laws Have Teeth—So Why Aren’t They Biting?
In November 2022, then-Sex Discrimination Commissioner Kate Jenkins explained why sexual harassment in Australian workplaces continues to happen. Basically, she said this was because the sex discrimination laws were reactive to a worker complaint and placed no duty on employers to prevent these types of incidents. But there is more to it than that, and the recent imposition of a positive duty under sex discrimination laws is still not preventing work-related harm.