The State of Victoria had a big week on mental health, with the Labor Government allocating billions of dollars to the improvement of the mental health of its citizens. Much of the justification for the spend (and the imposition of a mental health levy on large companies) is in response to the recent Royal Commission into Mental Health Systems. Workplace health and safety was on the agenda in that Royal Commission. Hence, it is worth looking at how, or if, this recent Budget helps employers improve the psychological health of their workers in anticipation of new regulations on this hazard promised by Victoria’s Minister for Workplace Safety, Ingrid Stitt.
Category: workplace
New workplace mental health info but no new strategy
On May 20, 2021, Australia’s Work Health and Safety (WHS) Ministers to discuss a range of occupational health and safety (OHS) matters. One matter will be the inclusion of a specific requirement on employers that, according to the Australian Council of Trade Unions (ACTU):
“…. would finally require employers to identify and address risks to mental health, in the same way, they are required to with risks to physical health.”
What the ACTU fails to make clear is why this regulatory change is required when the duty to provide a physically and psychologically safe and healthy workplace already exists in the current OHS/WHS laws in Australia.
The ACTU does, however, with the help of the Australia Institute and Centre for Future Work, provide more data on work-related mental health. The union movement is one of the few voices that acknowledge the structural elements of OHS but fails to consider any options other than regulation and, with a federal conservative government in power, it is unlikely to receive an attentive audience.
Twelve months of work-related deaths
In 2008, prominent occupational health and safety (OHS) advocate, Hilda Palmer wrote about the inadequate estimates of work-related deaths in the United Kingdom. Keeping work-related death confined to traditional categories provides a false understanding of the reality of OHS. Palmer wrote:
“Far from being complacent about the health and safety record in this country, we need to be honest and open, and examine what is really going on”.
Recently, at the 2021 Workers Memorial, a representative of the Victorian Trades Hall read out a list of those who have died at, or due to, work in the last 12 months. It was a list of 47 people. The categories have expanded to include truck incidents, asbestosis, silicosis as well as the more traditional traumatic injuries. Curiously no suicides. A transcripted list of those 47 is below.
Continue reading “Twelve months of work-related deaths”Resilience = the enemy of the Duty of Care
Last year Professor Michael Quinlan and Dr Elsa Underhill wrote about how precarious work arrangements had contributed to the spread and prevalence of COVI19 in Australia and its workplaces. Soon Australia’s Treasurer, Josh Frydenburg, will announce his 2021-22 Budget strategy. It is forecast to include big government spending and in many different areas of Australian industry, but the economy and Australians’ health may be better served by addressing the precarious employment structures on which more and more businesses rely and about which the Government seems disinterested.
In the latest edition of Griffith Review (no. 72), Angela Smith looked at how embedded precarious work is in Australia’s economic rebound. She also looked at how the wellbeing and wellness industries compound the health and safety risks of this type of work in this time of COVID19.
The economy is King
There has been discussion over many years about the business case for occupational health and safety (OHS). Several academics have attempted to quantify the financial benefits of good OHS management and systems. Business does not operate in a political or economic vacuum but it is possible to think it does when the OHS profession is so quiet on socioeconomic elements.
Australia and many other countries operate in a neoliberal economic and political system that provides OHS benefits and harms. The OHS context is touched on occasionally in public forums but the size of the challenge for structural and organisational change in Australia is perhaps best illustrated by an excerpt of Prime Minister Scott Morrison‘s presentation to the West Australian Chamber of Commerce and Industry on April 14, 2021. When asked about his priorities as Prime Minister he said:
The hill that OHS needs to climb for respectability remains a mountain
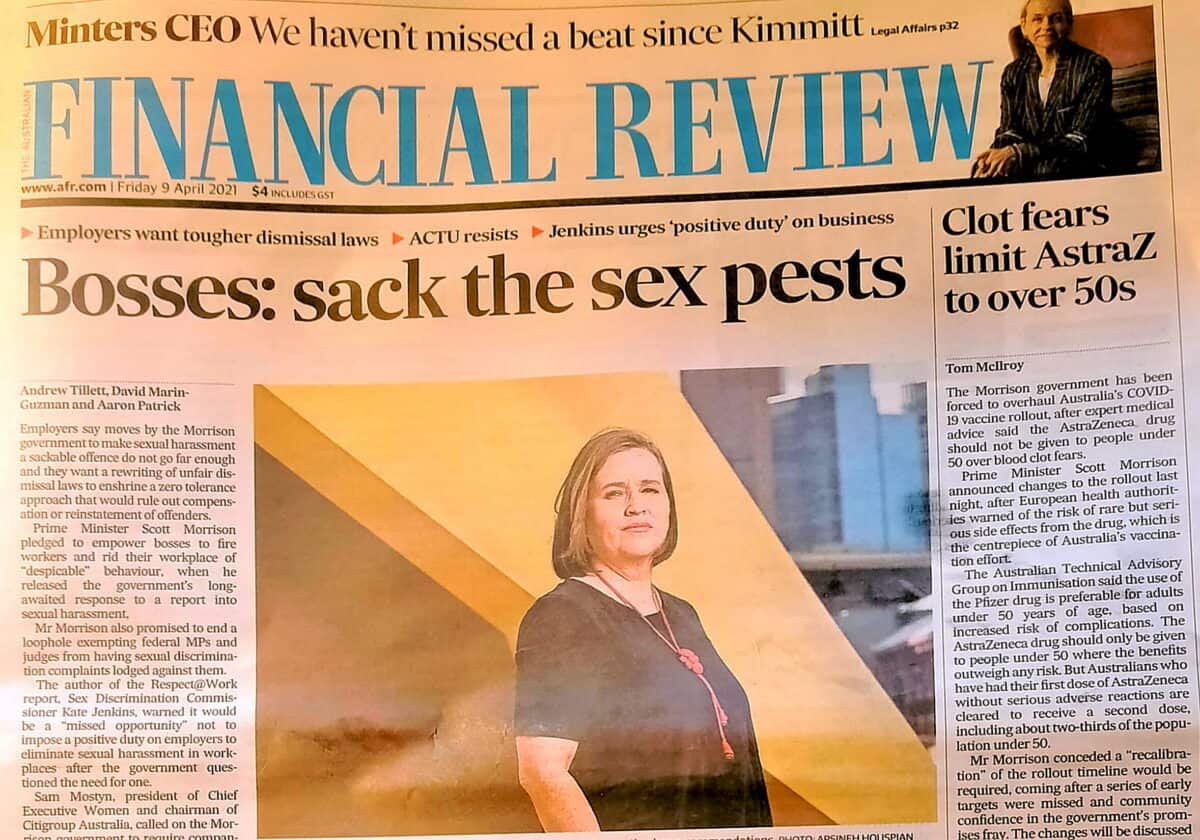
The current Australian debate about sexual harassment at work illustrates the forces ranged against occupational health and safety (OHS) being seen as a legitimate approach to preventing psychological harm. Entrenched Industrial Relations perspectives appear to be the biggest barrier. Such barriers are not always intentional and have evolved over years and decades as cultures and ideologies do. Some of the recent media coverage on the release of the Federal Government’s response to the report of the 2020 National Inquiry into Sexual Harassment in Australian Workplaces illustrates the dominance of industrial relations thinking – part of the reason Sex Discrimination Commissioner Kate Jenkins has described elements of the government’s response as a missed opportunity.
The OHS profession must start to overtly tackle each of these dominant perspectives.
Should we feel safe or be safe?
A major impediment to establishing safe and healthy workplaces is that there is a widespread expectation for everyone to feel safe at work. Yet, the legislative occupational health and safety (OHS) obligation on employers and workers is for them to be safe. It is a significant difference, for the former addresses perception, and the latter requires action.
Recently the Australian Government responded to a major inquiry into sexual harassment at work. Attorney-General Michaelia Cash, launching the official response with Prime Minister Scott Morrison, said:
“In terms of sexual harassment in the workplace, I think we’d all agree – in fact, it needs to be just a basic fundamental – everybody has the right to feel safe in the workplace.”