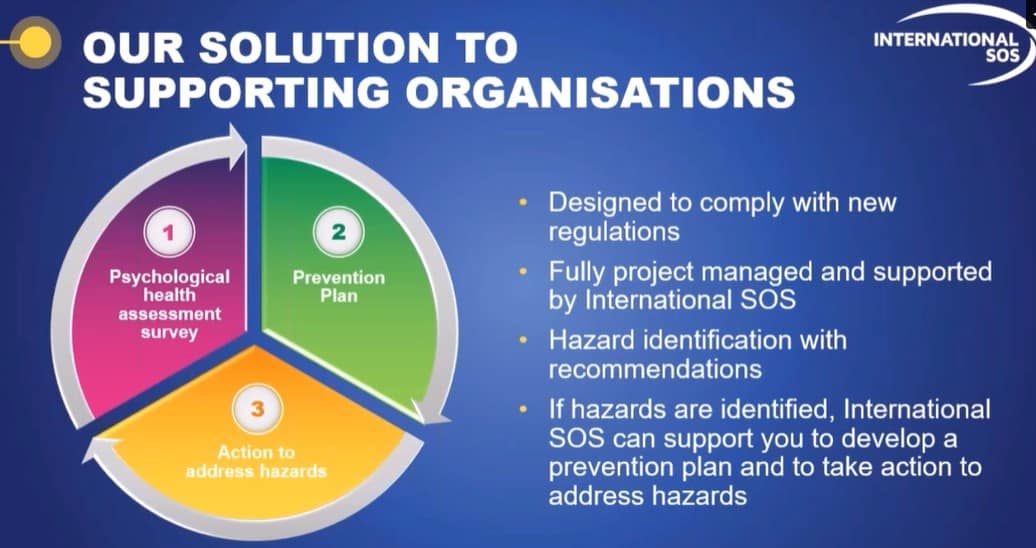
Recently International SOS conducted a webinar on workplace psychosocial hazards and controls. Parts of it were clearly marketing and promotional, but some of the speaker’s content was fascinating and useful.
The seminar’s structure was good because it included a global perspective and a local Australian. The speaker from a worldwide standpoint, Dr Rachel Lewis, used financial figures to illustrate the seriousness of workplace mental health risks. These involved annual costs to employers, costs of workplace stress and other figures in the billions. This approach encourages a misunderstanding of the audience for workplace mental health seminars and the occupational health and safety (OHS) approach to the hazard.